Reducing Equipment Downtime Through Maintenance

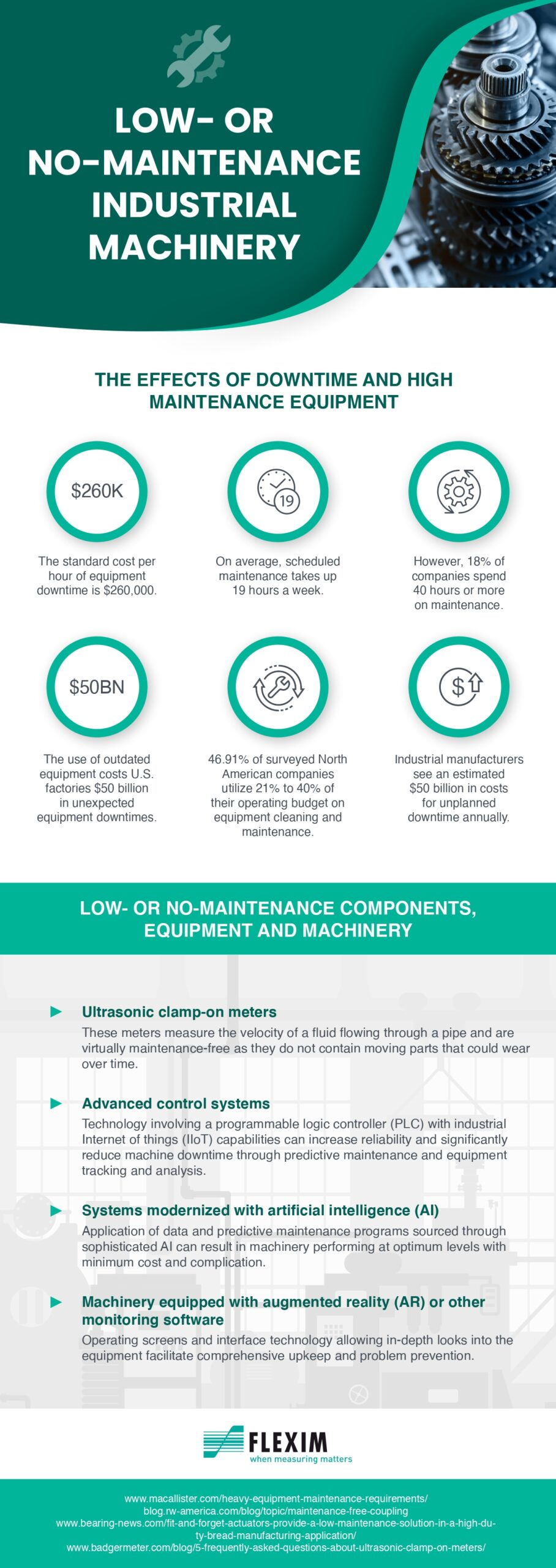
Maintenance expenditures for equipment can pile up, both financially and in terms of time. How do you stay competitive while also producing a return on investment (ROI)? This section focuses on the administrative procedures and technological advancements utilized to reduce equipment and maintenance downtime.
The market for maintenance, repair, and operations is expected to be valued $701.3 billion by 2026. A variety of elements in industrial settings contribute to this high cost. The great majority of unplanned downtime is caused by out-of-date resources. Unexpected equipment downtime, according to maintenance professionals, can be caused by machine failure, human mistake, insufficient maintenance time, and poor design.
Using parts that require little to no maintenance is an efficient approach to save money on maintenance. Clamp-on ultrasonic meters are one example. Because they have no moving parts that degrade with time, these meters are used in a number of settings, including the water distribution industry. They are intended to require little or no maintenance.
Another option to increase ROI is to implement a preventative maintenance (PM) strategy. Indeed, 76% of industrial enterprises prioritized preventive maintenance for 2020. This strategy seeks to identify and handle possible problems before they become a problem. As a result, PM decreases downtime, increases equipment life, and raises resale value. However, the type of asset has an effect on the overall cost of ownership.
Analytical technologies are also used in predictive maintenance. According to studies, 41% of industrial businesses already use this method. Despite being more expensive and a newer concept, predictive maintenance can be extremely cost-effective. According to the US Department of Energy, the potential savings from predictive maintenance to preventative maintenance range from 8 to 11%. According to predictions, the global market for predictive maintenance will be valued $23.5 billion by 2024.
The importance of predictive maintenance cannot be overstated (PdM). Predictive maintenance updates and analyzes the current state of the equipment using software, sensors, and artificial intelligence. Using the gathered data, it is possible to predict when equipment will require maintenance. In contrast to routine or time-based preventative maintenance, this strategy seeks to conserve money by only responding when absolutely necessary.
Maintenance management is a demanding endeavor. However, by adopting new technologies, updating to low- or no-maintenance components, and employing the proper tools for the job, common equipment’s lifespan and functionality can be extended.
The infographic contains additional information regarding maintenance and practical options.